
The electromagnetic flowmeter is composed of two parts: a sensor and a converter, and the sensor is composed of a measuring tube, an electrode, an excitation coil, an iron core, and a housing. After amplifying, processing and calculating the flow signal, the converter can display instantaneous flow, cumulative flow, output pulse, analog current and other signals for the measurement and control of fluid flow. The electromagnetic flowmeter adopts an intelligent converter, which not only has the functions of measurement and display, but also supports the functions of data remote transmission, wireless remote control, alarm and so on.
The electromagnetic flowmeter is suitable for conductive media with conductivity greater than 5uS/cm, wide nominal diameter range, adapts to various actual environmental conditions, has a variety of power supply modes, a variety of signal outputs, adopts standard RS-485 serial communication interface, pays for the international general standard MODBUS-RTU communication protocol and GPRS and other wireless and wired communication networking methods, and has a cumulative pulse equivalent output. Wireless meter reading systems (computer management software and databases) with remote network access are available.
Measuring principle
The working principle of electromagnetic flowmeters is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. In the figure below, the two electromagnetic coils at the upper and lower ends produce a constant or alternating magnetic field, when the conductive medium flows through the electromagnetic flowmeter, the induced electromotive force can be detected between the left and right electrodes on the tube wall of the flowmeter, and the size of the induced electromotive force is proportional to the flow rate of the conductive medium, the magnetic induction intensity of the magnetic field, and the width of the conductor (the inner diameter of the measuring tube of the flowmeter), and then the medium flow rate can be obtained through calculation.
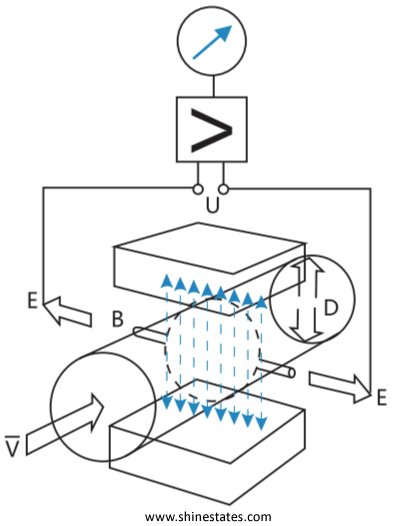
The equation for the process parameters of induced electromotive force is: E=KBVD
where E: induced electromotive force; D: Measuring the inner diameter of the tube; B: Magnetic induction intensity; V: average flow rate; K: Coefficients related to the distribution of the magnetic field and the axial length
Product Applications
■Petroleum, chemical, iron and steel
■Food, electricity, papermaking
■Water treatment, water supply, heating, environmental protection, etc
Basic parameters
| Enforce the standard | JB/T9248-1999 |
| Nominal diameter | 15-1200mm (Customizable) |
| Flow rate range | 0-10m/s |
| Accuracy | ±0.5%R,±1%R (DN20 or less) |
| Dielectric conductivity | Theoretical values>5uS/cm,Practical use>30uScm |
| Nominal pressure | 1.0、1.6、2.5、4.0MPa |
| Ambient temperature | -10℃~55℃ |
| Lining material: neoprene(CR) | Extreme temperatures 0~+80℃ |
| Lining material: PTFE | Extreme temperatures 0~+120℃ |
| Lining material: FEP | Extreme temperatures 0~+120℃ |
| Lining material: PFA | Extreme temperatures -10~+180℃ |
| Lining material: PU | Extreme temperatures -20~+60℃ |
| Output signal | 4-20mA;Pulse/Frequency 2kHz (default),5kHz(Max) |
| Cable port size | M20×1.5(Nylon waterproof connector is standard, explosion-proof metal connector is optional) |
| Supply voltage | 110/220V AC(100-240V AC),50Hz/60Hz;24V DC±10% Power consumption:<15VA |
| Communication method | RS-485,MODBUS-RTU Protocol、HART Protocol; GPRS |
| Signal electrode and ground electrode materials | SUS316L, Hastelloy C, Hastelloy B, titanium, tantalum, platinum, tungsten carbide |
| Electrode form | Interpolated |
| Number of electrodes | 3-4 electrodes (2 measuring electrodes + 1 ground electrode), configured according to caliber |
| Housing material | Carbon steel, stainless steel |
| Ingress protection | Split type (IP65, IP67, IP68); All-in-one (IP65) |
| Spacing/Wiring Length (Split) | Standard 10m connecting line, optional 1~300m |